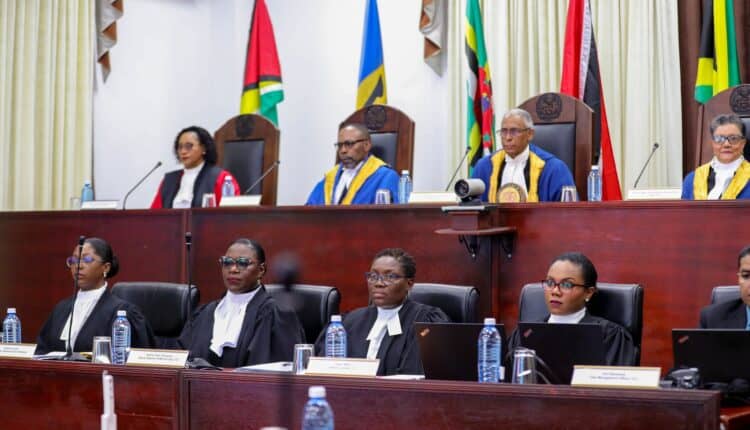
On Wednesday, 21 June 2023, the Caribbean Court of Justice (CCJ), sitting in Guyana, delivered its judgment for the special leave application, AB v The Director of Public Prosecutions [2023] CCJ 8 (AJ) GY.
The CCJ denied the Applicant special leave to appeal to the CCJ to review a decision of the Court of Appeal of Guyana, which had affirmed the imposition of two concurrent life sentences on him.
The Applicant will be eligible for parole after serving 20 years of the sentence.
The Applicant was charged with two counts of sexual activity with a child contrary to the Sexual Offences Act of Guyana.
He was convicted in 2018 and immediately sentenced by the Mme. Justice Jo-Ann Barlow to two concurrent life sentences, with 20 years to be served before his eligibility for parole.
He appealed his conviction and sentence to the Court of Appeal in 2018.
Subsequently, the Court of Appeal delivered a unanimous judgment, dismissing his appeal and affirming his conviction and sentence.
The Applicant then applied for special leave to appeal to the CCJ.
He contended that his sentence was manifestly excessive and that the sentencing process of Justice Barlow was flawed.
He also contended that the Court of Appeal’s failure to review and correct these errors, amounted to a serious miscarriage of justice which justified the granting of special leave by the CCJ.
In a judgment authored by Justice Jamadar, the CCJ held that the principal question for determination was whether the Applicant satisfied the requirements of special leave.
In order to be granted special leave, the Applicant was required to show that there was a realistic possibility that a serious miscarriage of justice may have occurred.
According to the CCJ, in order to satisfy this test, the Applicant was required to make an arguable case that the sentence imposed was manifestly excessive and that the judicial sentencing process did not sufficiently meet acceptable fair hearing standards, in order to avoid any serious miscarriages of justice.
Examining the sentencing process, the CCJ noted that in its judgment in Pompey v The Director of Public Prosecutions, guidance was provided to trial judges on the best practices to be followed in cases involving sexual violence on minors.
In another judgment, Ramcharran v The Director of Public Prosecutions, the Court affirmed these best practices with an expectation that they will be applied as and when appropriate.
Ideally, this guidance ought to be followed to ensure that constitutional standards for a fair hearing are satisfied.
However, failure to do so was not fatal. The CCJ noted that these cases were not yet decided when Justice Barlow sentenced the Applicant.
In the Applicant’s case, Justice Barlow did not receive a victim impact statement; sentenced him immediately after the verdict was given and did not consider a social services report.
However, the CCJ was of the view that it was evident that she considered the aggravating factors placed before her, including the young age of the complainant, the lack of a guilty plea, the Applicant’s attempt to shift blame, the repeated course of conduct, and the consequential emotional damage to the complainant.
Based on these, and after having heard and considered the Applicant’s plea in mitigation, Justice Barlow determined that in the exercise of her discretion, she could not be lenient.
Her approach demonstrated an intention to consider and balance relevant sentencing factors, though not necessarily as fully as advised in Pompey and Ramcharran.
Her sentencing remarks also showed that the Applicant’s rehabilitation and re-integration into society were taken into account.
With respect to his sentence, the CCJ noted that life imprisonment was the maximum penalty under the relevant section of the Sexual Offences Act and was within the range of punishment options available to Justice Barlow.
The CCJ also found that the circumstances of the crime were well placed before Justice Barlow, who found no mitigating circumstances.
Importantly, the CCJ observed that what made this case distinct in its severity was the special relationship of trust between the complainant and the Applicant, and the young age of the former.
In addition, there were several precedents where those convicted of the crime of sexual activity and who were adults in positions of trust like the Applicant, were given life imprisonment sentences.
So, in his case, the Applicant’s sentence was neither extraordinary nor manifestly excessive.
In conclusion, the CCJ held that while the sentencing approaches and recommendations made in Pompey and Ramcharran were not precisely followed, it did not necessarily mean that Justice Barlow in the exercise of her sentencing discretion, and the Court of Appeal in its review of the process, erred in law and in fact so as to create any serious manifest injustice or miscarriage of justice.
Consequently, the CCJ dismissed the application for special leave and ordered that each party should bear its own costs.
The matter was determined by Justices Maureen Rajnauth-Lee, Denys Barrow and Peter Jamadar.
Nigel Hughes, Ronald Daniels, Savannah Barnwell, Kiswana Jefford and Shawn Shewram represented the Applicant, and Teshana Lake, Assistant DPP and Diana O’Brien, Assistant DPP represented the Office of the Director of Public Prosecutions.
The full judgment of the Court and judgment summary are available on the CCJ’s website at ccj.org.
CLICK HERE TO JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP
CLICK HERE TO JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP
CLICK HERE TO JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP
CLICK HERE TO JOIN OUR WHATSAPP GROUP
Advertise with the mоѕt vіѕіtеd nеwѕ ѕіtе іn Antigua!
We offer fully customizable and flexible digital marketing packages.
Contact us at [email protected]