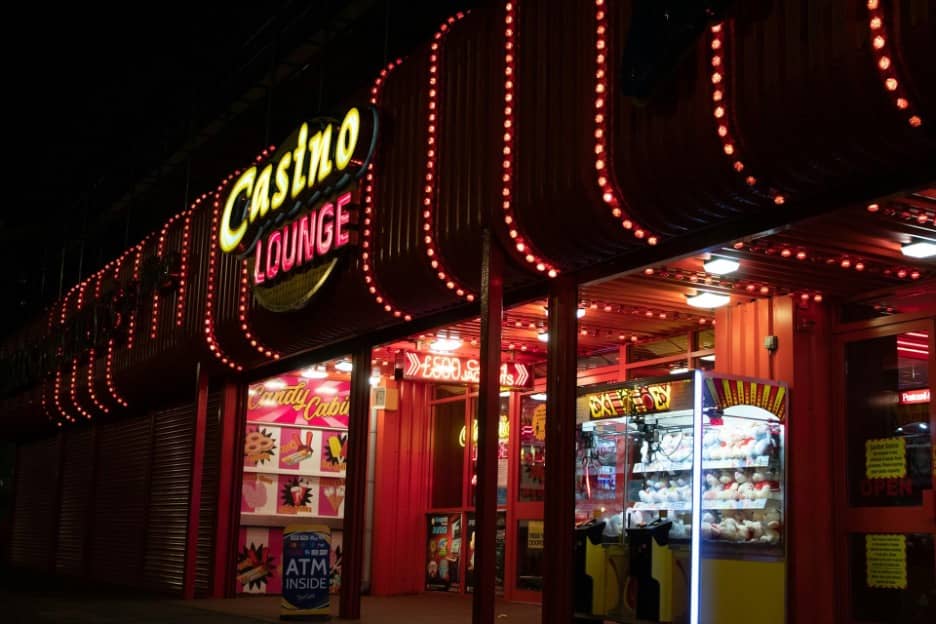

Gambling regulations vary significantly around the world, from highly permissive to strictly prohibited. Two intriguing case studies are the Caribbean nation of Antigua and Barbuda and the United States. While both allow gambling in various forms, their regulatory approaches differ in notable ways. Let’s take a closer look at the gambling landscapes in these two countries.
Antigua and Barbuda: A Pioneering Gambling Jurisdiction
Antigua and Barbuda was one of the first countries to embrace online gambling, beginning to issue licenses to non-resident casino operators in 1994. The island nation’s Financial Services Regulatory Commission (FSRC) oversees two types of licenses:
- Interactive Gaming License – covers online casinos, poker, slots, lotteries, etc. Requires certification of the random number generator (RNG) software used.
- Interactive Wagering License – for online sportsbooks and betting. Does not involve an RNG but rather software for calculating odds and payouts.
To obtain a casino license, applicants pay a $15,000 setup fee and an annual $100,000 renewal fee. Lawyers like those at Law&Trust International assist operators in navigating the licensing process, from entity formation to local bank account setup.
Antigua and Barbuda’s early entry into online gambling licensing stems partly from its status as a former British colony. Through legal agreements with the UK, it can offer lottery and other gambling products to British citizens. This historical relationship has helped position Antigua as an attractive base for gambling companies eyeing the lucrative UK market.
The USA: A State-by-State Approach
In contrast to Antigua’s unified national policy, gambling law in the USA is largely determined at the state level. The federal Wire Act of 1961, originally aimed at curbing mob-run gambling rings, prohibits interstate wagering. But a 2011 reinterpretation limited the act’s scope to sports betting, paving the way for states to legalize online casinos and poker.
Currently, online casino gambling is permitted in some form in six states:
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Michigan
- New Jersey
- Pennsylvania
- West Virginia
The latest to join the list is Rhode Island, where an online casino bill was signed in June 2023 and took effect on March 1, 2024.
Each state has its licensing requirements, typically including:
- Registering a legal entity in the state
- Partnering with a licensed land-based casino
- Undergoing extensive background checks and software testing
License fees and terms vary. In New Jersey, for instance, the fee is no lower than $400,000 for an initial 3-year license for internet gaming. In West Virginia, it’s $250,000 initially and $100,000 to renew.
Key Differences and Similarities
While both Antigua and the USA allow online gambling, their approaches differ in scope and specifics:
- Antigua has a unified national licensing system, while the USA leaves it to individual states.
- Antigua was an early mover in online gambling, while the USA has been more cautious, with only a handful of states legalizing it so far.
- Both have stringent licensing requirements, but the costs and procedures vary.
Interestingly, some US-based companies like FanDuel, with their offerings like FanDuel Casino: Real slots in PA are entering the online gambling space in states like Pennsylvania. This reflects the growing acceptance of online gambling in parts of the USA.
The Future of Gambling Regulation
As online gambling continues to grow globally, regulatory approaches will likely evolve. Smaller jurisdictions like Antigua may benefit from their agility and openness to the industry. Meanwhile, the USA’s state-by-state approach allows for experimentation and tailoring to local preferences, but may create a complex patchwork for operators to navigate.
Ultimately, both countries will need to balance consumer protection, tax revenue potential, and industry growth in their gambling policies. As more jurisdictions weigh the costs and benefits of legal gambling, the regulatory landscape will remain dynamic and diverse.
In conclusion, while Antigua and the USA have taken different paths on gambling law, both have found ways to permit and regulate online casinos and betting. As the industry expands, each country’s approach offers lessons for other jurisdictions grappling with the challenges and opportunities of gambling in the digital age. One thing seems certain: the global conversation around gambling regulation is far from over, with new developments unfolding all the time.
Advertise with the mоѕt vіѕіtеd nеwѕ ѕіtе іn Antigua!
We offer fully customizable and flexible digital marketing packages.
Contact us at [email protected]
















Like any other independent country Antigua and Barbuda is a sovereign legal jurisdiction. That means the laws of Antigua and Barbuda Govern its people and territory. We cannot therefore be subject to any other state or country’s laws. That is the mean reason why we won our case at the WTO. America has sign on to these treaties but when it comes to it they do not adhere to it’s rules and principles. They are a law above itself. That is why they do not sign on to the ICC. This world order needs to change. It cannot be just a law for some and not for all.
Comments are closed.