
Farming Techniques in the Caribbean and Antigua & Barbuda: Tradition, Sustainability, and Innovation
By: Tyreke G Thomas-Horsford
Agriculture in the Caribbean is a story of resilience, adaptation, and innovation. From centuries-old practices rooted in colonial history to cutting-edge technologies like drone farming, the region’s farmers have continually evolved to meet the challenges of climate change, limited land resources, and food security. Antigua and Barbuda, like many of its neighbors, exemplifies this blend of tradition and modernity, showcasing how diverse farming techniques can sustain communities and economies.
Traditional Foundations
Caribbean agriculture has long relied on practices passed down through generations:
Sugarcane Cultivation: Once the backbone of Antigua’s economy, sugarcane plantations shaped land use and trade for centuries. Though diminished today, they remain part of the agricultural heritage.
Mixed Crop Farming: Farmers traditionally grow cassava, maize, pigeon peas, yams, and sweet potatoes together. This intercropping system improves soil fertility, reduces pest risks, and ensures food security.
Pastoral Farming: Livestock rearing—cattle, goats, sheep, and poultry—provides meat, milk, and eggs. It remains vital, though overgrazing can lead to land degradation.

Climate-Smart Agriculture
With rising temperatures, unpredictable rainfall, and stronger hurricanes, Caribbean farmers are adopting climate-smart strategies:
Crop Diversification: Mixing crops reduces vulnerability to extreme weather and market fluctuations.
Drought-Resistant Varieties: Research institutions promote cassava, rice, and corn strains that thrive in dry conditions.
Water Management: Rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation, and mulching are critical in Antigua and Barbuda, where freshwater resources are limited.
Soil Conservation: Techniques such as contour farming, cover crops, and mulching reduce erosion and maintain fertility.
Sustainable Innovations
Modern Caribbean agriculture increasingly emphasizes
sustainability:
Agroforestry: Integrating fruit trees with crops and livestock improves biodiversity, stabilizes soils, and provides protection against hurricanes.
Agroecology: Farmers adopt ecological principles, focusing on reduced chemical use and community involvement.
Biofertilizers and Biopesticides: Natural alternatives enhance soil health and reduce environmental damage.
Integrated Farming Systems
Island nations with limited land are adopting integrated systems to maximize efficiency:
Aquaponics: Combining fish farming with plant cultivation maximizes resource use and provides dual outputs of vegetables and fish.
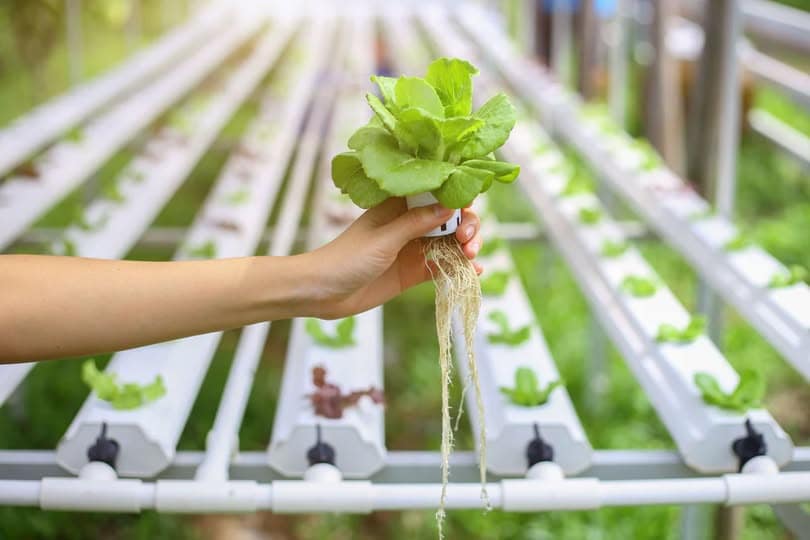
Hydroponics: Soil-less farming using nutrient-rich water solutions is gaining popularity, especially in Antigua’s urban and water-scarce areas.
Mixed Farming: Many smallholders combine crops and livestock to diversify income and optimize land use.
Drone Farming: The New Frontier
One of the most exciting developments in Caribbean agriculture is the use of drones. These unmanned aerial vehicles are revolutionizing farming by providing real-time data and precision management:
Crop Monitoring: Drones detect plant stress, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies early.
Precision Spraying: Targeted pesticide and fertilizer application reduces costs and environmental impact.
Mapping and Planning: High-resolution aerial imagery helps design efficient planting and irrigation systems.
Data Integration: Farmers use drone data for yield forecasting, soil management, and disaster recovery after hurricanes.
Drone farming is particularly valuable in Antigua and Barbuda, where smallholder farms dominate. It allows farmers to maximize productivity on limited land, reduce waste, and adapt quickly to changing conditions.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite these advances, Caribbean agriculture faces hurdles:
High Costs: Modern technologies like hydroponics and drones require significant investment.
Training Needs: Farmers must be equipped with knowledge to use new tools effectively.
Policy Support: Governments play a crucial role in providing incentives, subsidies, and education to encourage sustainable practices.
Yet, the opportunities are immense. By combining traditional wisdom with modern innovation, Caribbean farmers can build resilient systems that ensure food security, protect ecosystems, and strengthen local economies.
Conclusion
Antigua and Barbuda’s agriculture is evolving from its colonial sugarcane roots to a diverse, modern system that blends traditional practices with climate-smart and high-tech innovations. Across the Caribbean, farmers are embracing sustainability and technology—from intercropping and agroforestry to hydroponics and drone farming. Together, these techniques position the region to meet the challenges of climate change, reduce reliance on imports, and create a more secure and sustainable agricultural future.
Advertise with the mоѕt vіѕіtеd nеwѕ ѕіtе іn Antigua!
We offer fully customizable and flexible digital marketing packages.
Contact us at [email protected]
















We can do this!
Comments are closed.